Types of Cyber Crimes & IPC Sections
Cyber Crime is not defined in Information Technology Act 2000 nor in the I.T. Amendment Act 2008
nor in any other legislation in India. In fact, it cannot be too. Offence or crime has been dealt with
elaborately listing various acts and the punishments for each, under the Indian Penal Code, 1860 and
quite a few other legislations too. Hence, to define cyber crime, we can say, it is just a combination of
crime and computer.
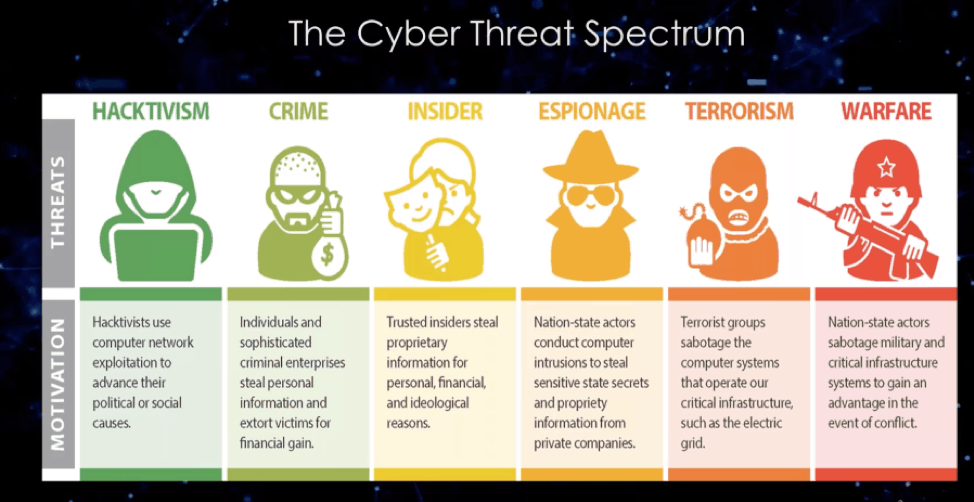
Different types of cybercrimes have different punishments in India.
Identity theft - When personal information of a person is stolen with the purpose of using their financial resources or to take a loan or credit card in their name then such a crime is known as Identity theft.
Cyberterrorism - When a threat of extortion or any kind of harm is being subjected towards a person, organization, group or state, it is known as the crime of Cyber Terrorism. Generally, it includes the well-planned attack strategies on the Government and corporate computer system.
Cyberbullying - When a teenager or adolescent harasses, defames, or intimidates someone with the use of the internet, phone, chat rooms, instant messaging or any other social network then the person is said to be committing the crime of Cyberbullying. When the same crime is done by adults it is known as Cyberstalking.
Harassment and Stalking - Harassment and stalking are prohibited over internet platforms as well. Cyber laws protect the victims and prosecute the offender against this offence.
Hacking - The most common cybercrime is Hacking. In this crime, the person gets access to other people's computers and passwords to use it for their own wrongful gain.
Defamation - While every individual has his or her right to speech on internet platforms as well, but if their statements cross a line and harm the reputation of any individual or organization, then they can be charged with the Defamation Law.
Copyright - With the massive surge in internet users, when the data/ information is distributed on all platforms, copyrighting your work aids you to restrict the use of your work. Any use of your copyrighted without your permission is a punishable offence.
Trade Secrets - Internet organization spends a lot of their time and money in developing softwares, applications, and tools and rely on Cyber Laws to protect their data and trade secrets against theft; doing which is a punishable offence.
Freedom of Speech - When it comes to the internet, there is a very thin line between freedom of speech and being a cyber-offender. As freedom of speech enables individuals to speak their mind, cyber law refrains obscenity and crassness over the web.
IPC Sections:
Section 43: Data theft
Section 65: Tampering with source documents is dealt with under this section.
Section 66: Computer related offences are dealt with under this Section.
66A Sending offensive messages thro communication service - jail for 3 years and 1 lakh fine or both.
66B Dishonestly receiving stolen computer resource or communication device with punishment upto
three years or one lakh rupees as fine or both.
66C Electronic signature or other identity theft like using others’ password or electronic signature etc.
Punishment is three years imprisonment or fine of one lakh rupees or both.
66D Cheating by personation using computer resource or a communication device shall be punished
with imprisonment of either description for a term which extend to three years and shall also be liable to
fine which may extend to one lakh rupee.
66E Privacy violation – Publishing or transmitting private area of any person without his or her consent
etc. Punishment is three years imprisonment or two lakh rupees fine or both.
66F Cyber terrorism – Intent to threaten the unity, integrity, security or sovereignty of the nation and
denying access to any person authorized to access the computer resource or attempting to penetrate or
access a computer resource without authorization. Acts of causing a computer contaminant (like virus
or Trojan Horse or other spyware or malware) likely to cause death or injuries to persons or damage to
or destruction of property etc. come under this Section. Punishment is life imprisonment.
Section 67 deals with publishing or transmitting obscene material in electronic form. The earlier
Section in ITA was later widened as per ITAA 2008 in which child pornography and retention of
records by intermediaries were all included.
Section 67-A deals with publishing or transmitting of material containing sexually explicit act in
electronic form. Contents of Section 67 when combined with the material containing sexually explicit
material attract penalty under this Section.
Section 69: This is an interesting section in the sense that it empowers the Government or agencies as
stipulated in the Section, to intercept, monitor or decrypt any information generated, transmitted,
received or stored in any computer resource, subject to compliance of procedure .
Section 69A inserted in the ITAA, vests with the Central Government or any of its officers
with the powers to issue directions for blocking for public access of any information through
any computer resource, under the same circumstances as mentioned above.
Section 69B
discusses the power to authorise to monitor and collect traffic data or information through any
computer resource.
No comments:
Post a Comment